Preparation of documentary evidence of transactions is important for a business. Business documentation serves several purposes such as accounting evidence, audit trail, adherence to other jurisdictional laws etc. The revenue generation function is one such area in which documentation is key. Whether the entity is a manufacturer, trader or service provider, the basis of its revenue generation is the sales it makes and the billing that it raises on its customers. It is on the basis of this sales billing that the entity receives money from its customers.
This article looks at meaning of and differences between two important steps in an entity’s sales and billing cycle- invoice and receipt.
Definitions and meanings
Invoice
An invoice is a document raised by a vendor on its customer indicating the nature of goods/services provided and the amount due for the same.
The key information that is usually found in an invoice is as follows:
- Name and address of the vendor
- Invoice number
- Invoice date
- Tax registration number of the vendor
- Customer name and address
- Nature of goods/service provided
- Quantity provided
- Rate
- Taxes charged
- Total amount invoiced
- Discount details if any
- Signature of the vendor
- Payment terms including credit period
- Payment details such as bank details
A proforma of an invoice is given below:
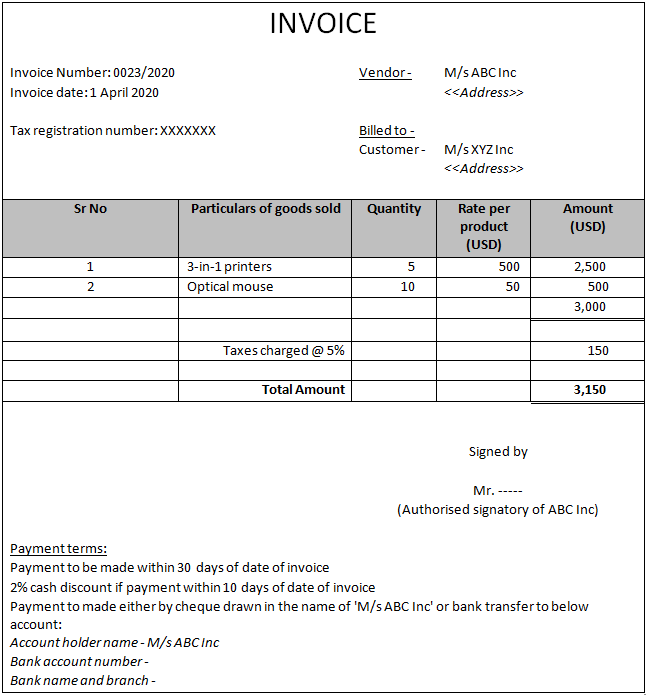
Issuing an invoice follows the provision of goods or rendition of services by the vendor. An invoice is categorized as an accounting document and serves as evidence of goods/ services provided and amounts receivable/payable. It is on the basis of an invoice that a seller records sale in its books and a customer records purchase in its books.
Receipt
A receipt is an acknowledgement document issued by the vendor to its customer confirming receipt of payment from the customer.
After invoicing of goods/services, vendors generally provide a credit period to its customer for payment of the invoices. When a customer clears the invoices by making payment, the vendor issues a receipt as an acknowledgement of the same. Receipt is often prepared and sent at the behest of the customer.
One receipt can be issued for payment against a single invoice or against payment for several invoices collectively.
A receipt typically includes the following details:
- Name of the vendor
- Name of the customer
- Receipt number
- Receipt date
- Amount received
- Mode of receipt
- Reference of invoice/s against which payment has been received
- Sign of vendor
A proforma of a receipt is given below:
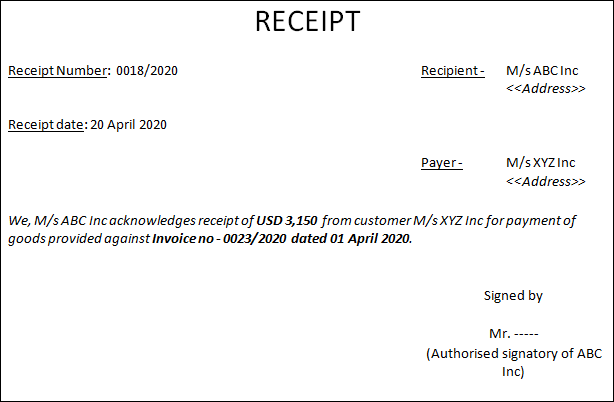
Difference between invoice and receipt
The key points of difference between invoice and receipt have been listed below:
1. Meaning
- An invoice is a legal document that evidences sale of goods by the vendor and indicates the amount payable by the customer for the sale transaction.
- A receipt is an acknowledgement document that confirms that the vendor has duly received payment against certain invoice/s from the customer.
2. Purpose
- The purpose of an invoice is to bill the customer and collect payment from the customer against goods sold/services provided.
- The purpose of the receipt is to acknowledge payment against invoice/s to the customer.
3. Timing of issued
- Invoice is issued by the vendor when goods are sold or services are provided i.e., as a precursor to payment
- Receipt is issued after payment is received by the vendor from the customer.
4. Sequence
- Invoice is generally the first document issued in the sales cycle.
- Receipt is generally the final document issued in the sales cycle.
5. Legality involved
- Invoice is a more formal legal document and its format may also be required to adhere to format as prescribed in jurisdictional laws, especially tax laws.
- A receipt is a less formal document in that it needn’t have any specific prescribed format mandated by the law.
6. Details included
- An invoice generally includes greater number of details from vendor and customer details to details of goods/services provided and amounts due.
- A receipt generally includes fewer details restricted to amount received and invoices against which payment has been received. Details of goods/services provided are generally not found in a receipt.
7. Accounting evidence
- Invoice serves as accounting evidence to record sales in the books of accounts of the vendor and to record purchases in the books of accounts of the customer.
- Receipt serves as an accounting evidence to the vendor for recording payment receipt in its books of account.
Conclusion – invoice vs receipt
While both invoice and receipt are issued by the vendor and sent to the customer, their purposes are completely different. While invoices are issued by vendors across categories, including both large and small vendors, formal receipts may be issued more by smaller vendors especially in case of cash receipts. In today’s day when books of accounts are predominantly digitized, larger vendors and customers can also rely on bank statements as proof of receipt/payment.
