The financial transactions among for-profit business organizations mostly take place on credit. When a business sells or buys goods on credit, the concept of debtors and creditors arises.
When goods are sold on cash basis there is no need to record the name of customers to whom goods are sold and only entries are made in cash account and sales account. Similarly in case of cash purchases, names of suppliers are not recorded. However, when goods are sold or bought on credit and payment is to be received or paid in future, the name of debtors or payables is necessary to record.
The terms debtors and creditors are mostly used in UK. The equivalent US terms are receivables and payables.
Definitions and meanings
Debtor
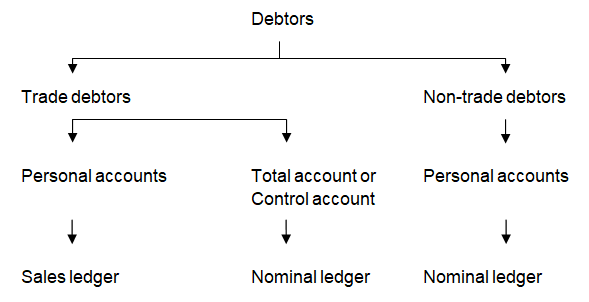
Debtor or receivable is an individual person or a business entity from whom we have a right to receive some amount of money or asset. Debtors normally arise when we sell goods or services on credit. Most of the business organizations trade on credit basis and buy and sell goods on credit. Apart from trading goods, non trading assets can also be sold on credit that also results in debtors. Debtor is an asset of the business and is recorded in current assets. Debtors are of two types:
- Trade debtors
- Non trade debtors
Trade debtors are those to whom we have sold trading goods or services. Trading goods are those which are sold in ordinary course of the business. A business may have many trade debtors to whom sales are made on regular basis and payments are also received on regular basis. Such debtors are recorded separately from others so that better controls can be exercised over them. When sales are made on credit it is recorded in form of double entry as:
Debtor account – [Dr.]
Sales account – [Cr.]
Non-trade debtors are those to whom we have sold non-trading goods. Non-trading goods are those which are not sold in ordinary course of a business. For example if a person is running a book shop, his trade is selling books and books are trading goods. If books are sold on credit to person, it will be called trade debtor. However, if he sells a computer that was being used in the shop to person on credit, it will be called non-trade debtor because computer is not a trading item or his primary business activities do not include selling computers. When a non trading asset like a computer is sold on credit is recorded in the form of double entry as:
Debtor account – [Dr.]
Asset account – [Cr.]
Complete record of all the debtors is maintained in the form of their personal accounts and also control accounts for trade receivables. Personal accounts for trade receivables are maintained in sales ledger whereas personal accounts of non trade debtors and control accounts of trade debtors are maintained in nominal ledger of the business.
Creditor
Creditor is a person or an entity from whom we have bought good on credit and payment of to be made. Credit is also called a payable. Creditors are also of two types:
- Trade creditors
- Non- trade creditors
Trade creditors are those from whom we have bought trading goods whereas non-trade creditors are those from whom we have bought non-trading goods. Trading goods are those which are bought for resale in ordinary course of the business. When trading goods are bought on credit, the double entry to record this purchase is:
Purchases account – [Dr.]
Creditor account – [Cr.]
When non-trading assets are bought on credit these are not recorded in purchases account and its double entry is:
Asset account – [Dr.]
Creditor account – [Cr.]
Like trade debtors, personal accounts of trade creditors are made in purchases ledger and control account is prepared in nominal ledger. Personal accounts of non trade creditors are also prepared in nominal ledger.
Difference between debtor and creditor
The major difference between debtor and creditor is explained below:
1. Nature
Debtor is a person from whom we have to receive some cash or asset and is a current asset of the business. Creditor is a person to whom we have to pay some cash or asset and is a current liability of the business.
2. Purpose
Purpose of a debtor is to record the amount of credit sales made to that person so that payment can be received in future. Purpose of a creditor is to record the credit purchases made from that person so that payment can be made in future.
3. Maintaining personal accounts
Personal accounts of trade debtors are maintained in sales or debtor’s ledger whereas personal accounts of trade creditors are maintained in purchases or creditor’s ledger.
4. Impact on profit
Debtor arises due to credit sales of the business and therefore increases sales and profit of the business. Creditor arises due to credit purchases of the business and therefore increases expenses and decreases profit of the business.
5. Impact on cash flows
Cash is received from debtors therefore it increase cash balances whereas cash is paid to creditors therefore it results in decrease in cash balances.
6. Impact on working capital cycle
Debtors increase the length of working capital cycle whereas creditors decrease the length of working capital cycle.
7. Impact on finance cost
Debtors show the free credit allowed to others and increase the finance cost whereas creditors show the free credit taken from others and decrease the finance cost.
Debtor vs creditor – tabular comparison
A tabular comparison of debtor and creditor is given below:
|
||||
| Nature | ||||
| Is a current asset | Is a current liability | |||
| Purpose | ||||
| Used to record credit sales | Used to record credit purchases | |||
| Maintaining personal accounts | ||||
| Maintained in debtors ledger | Maintained in creditors ledger | |||
| Impact on profit | ||||
| Increases profit | Decreases profit | |||
| Impact on cash flows | ||||
| Causes cash inflows | Causes cash outflows | |||
| Impact on working capital cycle | ||||
| Increases the length of working capital cycle | Decreases the length of working capital cycle | |||
| Impact on finance cost | ||||
| Increases the finance cost | Decreases the finance cost | |||
Conclusion – debtor vs creditor
Debtor and creditor are the accounting terms used for receivables and payables. Debtors are recorded as assets of the business whereas creditors are liabilities of the business. Debtors arise as result of credit sales whereas creditors arise as result of credit purchases made by the business.
